O_Fir滤波器的Verilog设计
Fir滤波器简介
FIR(Finite Impulse Response)滤波器:有限长单位冲激响应滤波器,又称为非递归型滤波器,是数字信号处理系统中最基本的元件,它可以在保证任意幅频特性的同时具有严格的线性相频特性,同时其单位抽样响应是有限长的,因而滤波器是稳定的系统。因此,FIR滤波器在通信、图像处理、模式识别等领域都有着广泛的应用。
5位直接型Fir滤波器结构
长度为M的因果有限冲激响应滤波器由传输函数H(z)描述: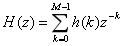
它是次数为M-1的z-1的一个多项式。在时域中,上述有限冲激响应滤波器的输入输出关系为: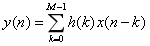 其中y(n)和x(n)分别是输出和输入序列。
其中y(n)和x(n)分别是输出和输入序列。
由Matlab得出五位Fir滤波器的Z域函数为: 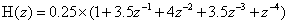
结构图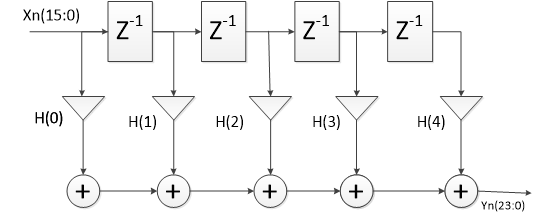
各模块设计
设计模块
寄存器
寄存器用于寄存一组二值代码,只要求它们具有置1、置0的功能即可。
本设计中使用带异步复位reset_n端的D触发器,当reset_n=1时,输出信号q_out=d_in,当reset_n=0且上升沿脉冲到达时q_out=0。
module Dff16(reset_n,clk,d_in,q_out);
input reset_n,clk;
input [15:0]d_in;
output reg [15:0]q_out;
always @(posedge clk or negedge reset_n)
begin
if(!reset_n)
q_out<=16'h0;
else
q_out<=d_in;
end
endmodule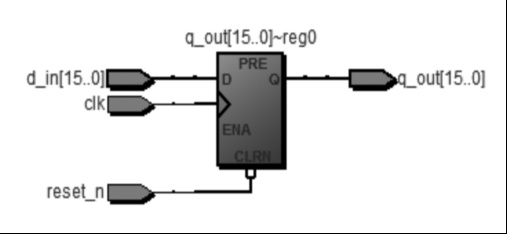
加法器
由于本设计只涉及到相加,而没有减法,所以本加法器实现两个32位无符号数的相加运算。
即将输入的两数,在时钟脉冲到来时相加运算,输出结果。
module add32(a,b,out);
input [31:0]a,b;
output [34:0]out;
assign out=a+b;
endmodule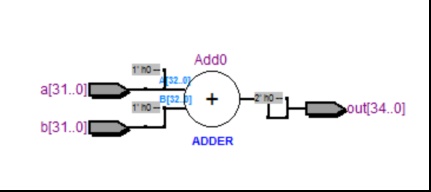
乘法器
从资源和速度考虑,常系数乘法运算可用移位相加来实现。
本设计采用加法树乘法器兼顾了资源与速度,将每个乘数例化了一个数组,然后移位相加得出乘积,这样使得乘法运算可以一个周期内完成。
module mult16(outcome,a,b);
input [15:0]a,b;
output wire [31:0]outcome;
wire [30:0] temp0;
wire [29:0] temp1;
wire [28:0] temp2;
wire [27:0] temp3;
wire [26:0] temp4;
wire [25:0] temp5;
wire [24:0] temp6;
wire [23:0] temp7;
wire [22:0] temp8;
wire [21:0] temp9;
wire [20:0] temp10;
wire [19:0] temp11;
wire [18:0] temp12;
wire [17:0] temp13;
wire [16:0] temp14;
wire [15:0] temp15;
assign temp15=mult16x1(a,b[0]);
assign temp14=((mult16x1(a,b[1]))<<1);
assign temp13=((mult16x1(a,b[2]))<<2);
assign temp12=((mult16x1(a,b[3]))<<3);
assign temp11=((mult16x1(a,b[4]))<<4);
assign temp10=((mult16x1(a,b[5]))<<5);
assign temp9=((mult16x1(a,b[6]))<<6);
assign temp8=((mult16x1(a,b[7]))<<7);
assign temp7=((mult16x1(a,b[8]))<<8);
assign temp6=((mult16x1(a,b[9]))<<9);
assign temp5=((mult16x1(a,b[10]))<<10);
assign temp4=((mult16x1(a,b[11]))<<11);
assign temp3=((mult16x1(a,b[12]))<<12);
assign temp2=((mult16x1(a,b[13]))<<13);
assign temp1=((mult16x1(a,b[14]))<<14);
assign temp0=((mult16x1(a,b[15]))<<15);
assign outcome=(temp0+temp1+temp2+temp3+temp4+temp5+temp6+temp7+temp8+temp9+temp10+temp11+temp12+temp13+temp14+temp15)/256;
endmodule乘法器测试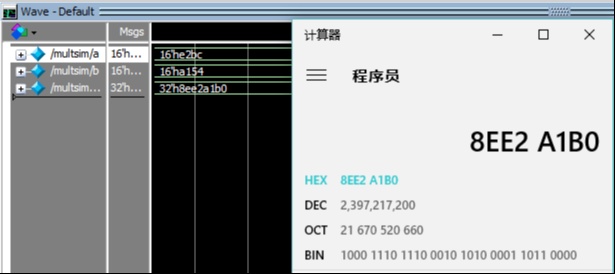
Verilog小数乘法实现方法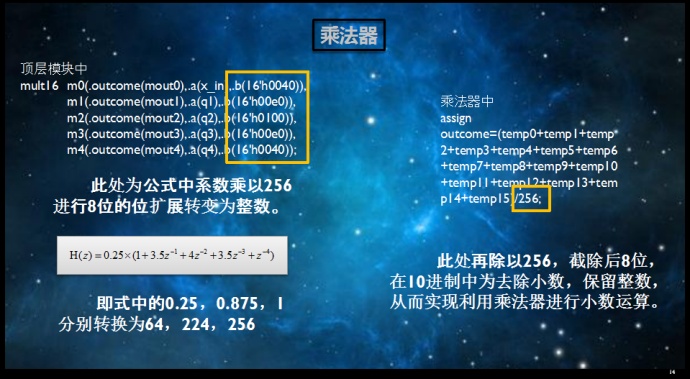
顶层模块
将3个16位寄存器,4个16位乘法器,3个32位加法器在顶层模块分别实例化。
module Fir(reset_n,clk,x_in,y_out);
input reset_n,clk;
input [15:0]x_in;
output [23:0]y_out;
wire [15:0]q1,q2,q3,q4;
wire [31:0]mout0,mout1,mout2,mout3,mout4;
wire [34:0]aout1,aout2,aout3,aout4;
dff16 D1(.reset_n(reset_n),.clk(clk),.d_in(x_in),.q_out(q1)),
D2(.reset_n(reset_n),.clk(clk),.d_in(q1),.q_out(q2)),
D3(.reset_n(reset_n),.clk(clk),.d_in(q2),.q_out(q3)),
D4(.reset_n(reset_n),.clk(clk),.d_in(q3),.q_out(q4));
mult16 m0(.outcome(mout0),.a(x_in),.b(16'h0040)),
m1(.outcome(mout1),.a(q1),.b(16'h00e0)),
m2(.outcome(mout2),.a(q2),.b(16'h0100)),
m3(.outcome(mout3),.a(q3),.b(16'h00e0)),
m4(.outcome(mout4),.a(q4),.b(16'h0040));
add32 a1(.a(mout0),.b(mout1),.out(aout1)),
a2(.a(aout1),.b(mout2),.out(aout2)),
a3(.a(aout2),.b(mout3),.out(aout3)),
a4(.a(aout3),.b(mout4),.out(aout4));
assign y_out=aout4[23:0];
endmodule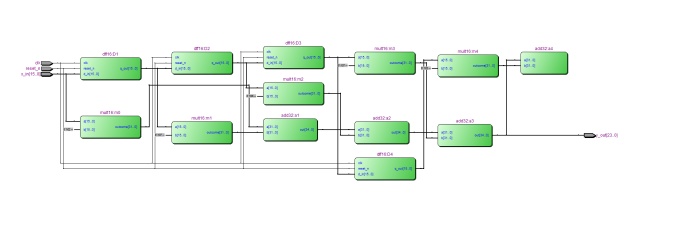
测试数据生成
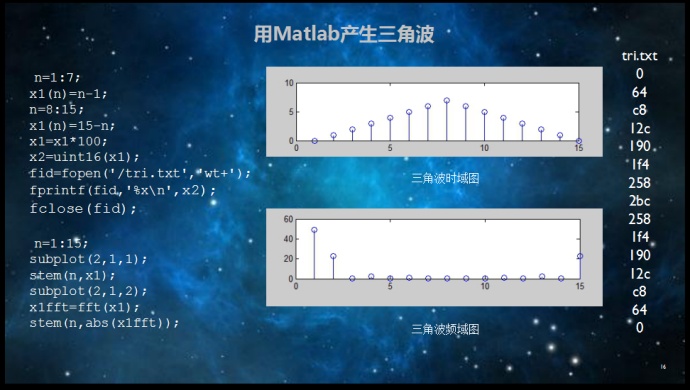
测试块
`timescale 1ns/1ns
`define clock 50
module test;
reg clk,reset_n;
reg [15:0]x_in;
reg [15:0]data_mem[0:15];
integer i;
wire [23:0]y_out;
always #`clock clk=~clk;
initial
begin
clk=0;
reset_n=1;
end
initial
begin
$readmemh("tri.txt",data_mem);
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge reset_n)
begin
if(!reset_n) begin
x_in<=15'b0;
i<=0;
end
else if(i<=13) begin
x_in<=data_mem[i];
i<=i+1;
end
end
Fir fir(.reset_n(reset_n),.clk(clk),.x_in(x_in),.y_out(y_out));
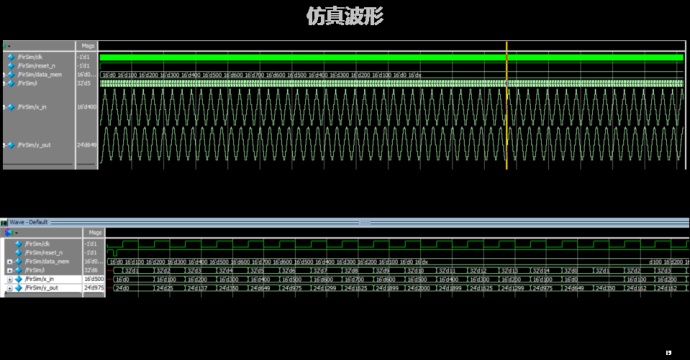
endmodule仿真及验证
仿真波形
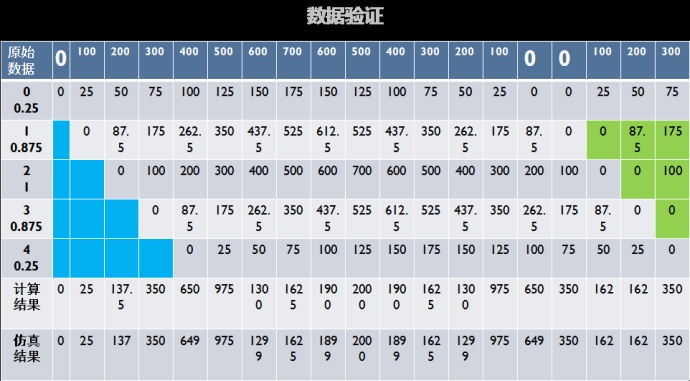
数据验证
参考文献:《高通FIR数字滤波器设计》,电子科技大学,周恒,《ASIC课程设计报告二》
演示PPT:5位Fir高通滤波器.pptx
评论已关闭